In this article, we are going to understand
What is Terraform resource block
Understand Terraform basic commands
terraform initterraform validateterraform planterraform applyorterraform apply -auto-approveterraform destroyorterraform destroy -auto-approve
Understand terraform resource behavior on executing terraform basic commands
Terraform Resource Block
A Terraform Resource is a fundamental unit used to model and manage infrastructure components.
Each resource block describes one or more infrastructure objects that you want to create, modify, or manage.
- Example: s3 bucket, ec2 instance, RDS instance, Security Group, VPC
-
resource "type" "name" { argument1 = "value1" argument2 = "value2" ......... = "......" ......... = "......" argumentn = "valuen" } Example of a Resource Block:
resource "aws_instance" "example" { ami = "ami-0c55b159cbfafe1f0" instance_type = "t2.micro" tags = { Name = "Linux" } }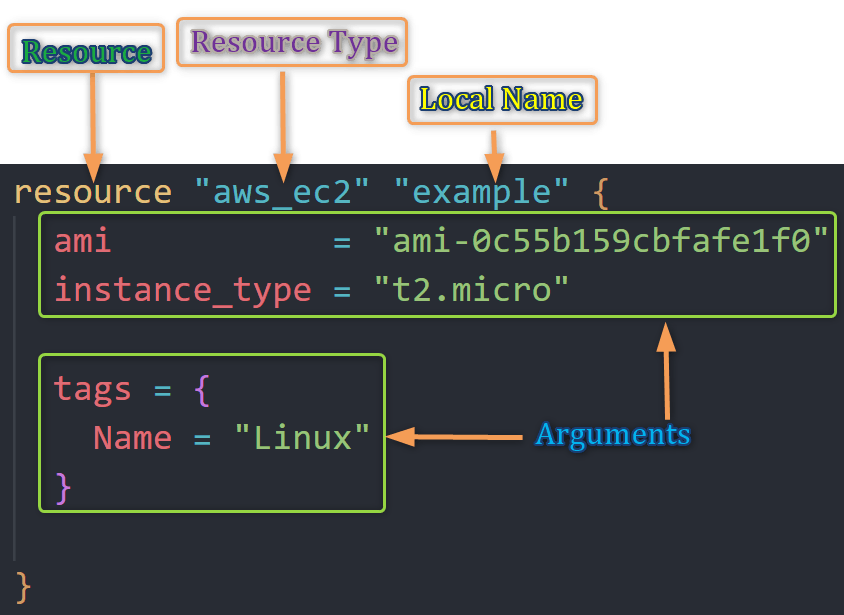
resource: The keyword to start a resource block.aws_instance:The resource type, which defines what you're creating (e.g., an AWS EC2 instance).
Resource type determines the kind of infrastructure object it manages and what arguments and other attributes the resource supports
example:The resource name is a unique identifier within your configuration.
It is a Local name ("example").
The name is used to refer to this resource from elsewhere in the same Terraform module but has no significance outside that module's scope.
ami,instance_typeandtags: Arguments or the Configuration parameters specific to the resource you're defining.
Terraform Resource Behaviors
Terraform resource behaviors refer to,
How Terraform manages and interacts with resources in your infrastructure.
These behaviors determine how resources are
created
destroyed
updated
Create :
Terraform attempts to create resources in your target infrastructure based on your configuration.
Terraform creates resources that exist in the configuration but are not associated(present) with a real infrastructure object in the state
Destroy :
Destroys resources that exist in the state/infra but no longer exist in the configuration.
Removing a resource from your Terraform configuration leads to the planned destruction of that resource in the infrastructure.
Update in-place :
update the resources whose arguments have changed
Terraform detects differences between the desired state in your configuration and the current state in the infrastructure. It plans and applies changes to update resources accordingly.
Destroy and re-create :
Terraform will destroy and re-create resources whose arguments have changed but which cannot be updated in-place due to remote API limitations
Example: Changing the Availability zone of an AWS EC2 instance
Dependency Management :
- Terraform ensures dependent resources are created or updated before resources that rely on them to avoid issues.
Concurrency Control :
- Terraform manages resource operation concurrency to prevent conflicts and ensure consistency.
State Management :
- Terraform maintains a state file that records the current state of the infrastructure, which is used to plan and apply updates.
Understanding Terraform Resource Behavior with Example
Let's Create an AWS EC2 instance and understand Terraform Resource(EC2) Behavior
Create a Terraform provider block
terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "~-> 5.0" } } } provider "aws" { region = "us-east-1" default_tags { tags = { terraform = "yes" project = "terraform-learning" } } }Create Resource (EC2) block
resource "aws_instance" "example" { ami = "ami-0df435f331839b2d6" instance_type = "t2.micro" tags = { Name = "Linux2023" Owner = "Venkatesh" } }
Let's Execute Terraform commands to understand resource behavior
terraform init: Initialize terraformThe
terraform initcommand is used to initialize a Terraform configuration.It sets up the necessary components and dependencies for Terraform to manage your infrastructure.
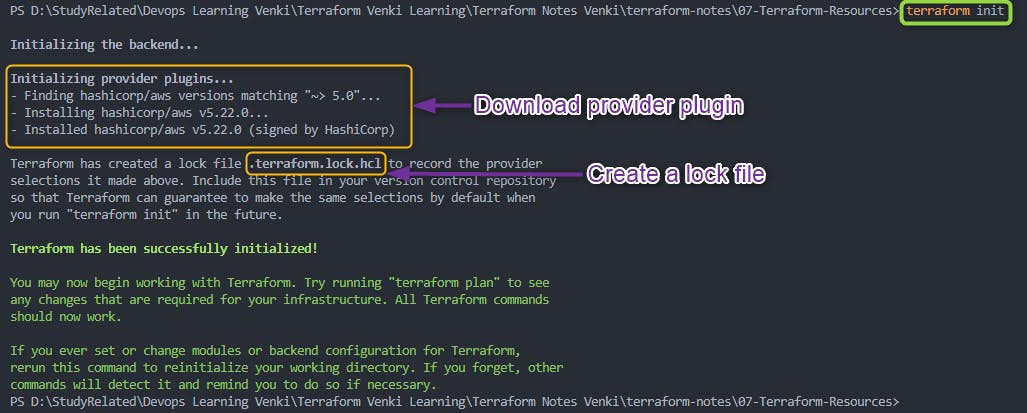
Downloading Providers and Modules: On executing
terraform initcommand terraform downloads the plugin for provider (in our case AWS) under .terraform folder in the current directory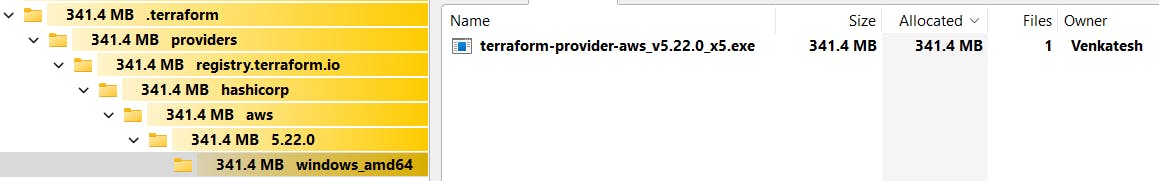
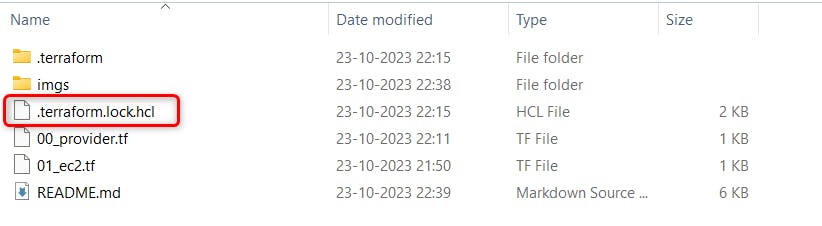
Locking and Tracking Dependencies: Terraform also creates a terraform.lock.hcl file to track provider and module versions.
terraform validate: Validate terraform codeValidate the configuration files in a directory
Validate runs checks that verify whether a configuration is syntactically valid and internally consistent
Primarily useful for general verification of reusable modules, including correctness of attribute names and value types.
It is safe to run this command automatically
Validation requires an initialized working directory (terraform init) with any referenced plugins and modules installed
Example :
terraform validate with error statements to correct
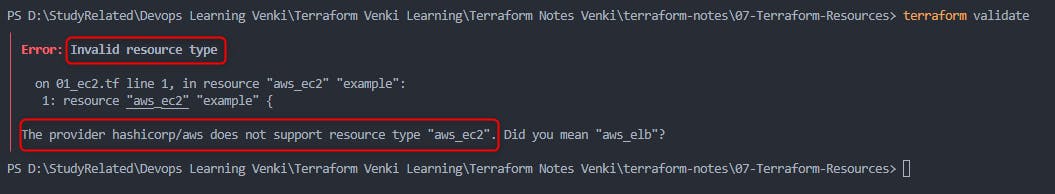
In the above case, resource should be
aws_instanceand notaws_ec2henceterraform validatewill show an errorterraform validate with no errors

terraform fmt: format terraform codeThe
terraform fmtcommand is used to automatically format Terraform configuration files, promoting consistent coding style and improved readability.Formatting: It standardizes the indentation, line breaks, and element ordering in your configuration files.
Syntax Rules: Enforces Terraform's syntax rules, ensuring proper indentation and formatting
Comments: Doesn't alter comments but ensures they are consistently styled.
It reformats files without changing the content or functionality of your configuration and is saved to run the command anytime
when
terraform fmtis executed, it lists the files that it formatted, if no files are listed it means all files are well formatted.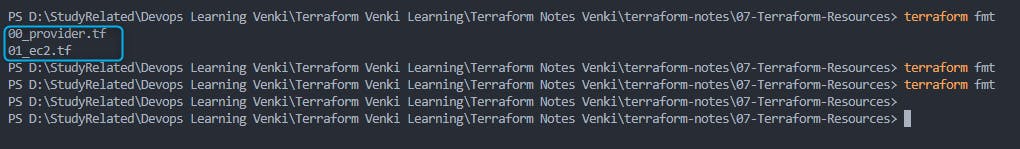
terraform plan: Review the terraform planThe
terraform plancommand is used to create an execution plan for your Terraform configuration, showing the changes Terraform will make to your infrastructure.Plan Infrastructure Changes: Compares the current state of your infrastructure to the desired state and plans the necessary changes.
Output Summary: Provides a human-readable summary of the planned changes, including creation, modification, and destruction of resources.
Detailed Information: Offers detailed information about planned changes, resource modifications, and dependencies.
Validation: Validates (
terraform validate) your configuration for syntax errors and inconsistencies before applying changes.Dry Run:
terraform planis a "dry run" command; it shows proposed changes without applying them.It's safe to execute this command
terraform planwill require you to have your AWS Credentials set and you can connect/access your AWS infrastructure. You will receive the below error when AWS cred are not set
Error: No valid credential sources found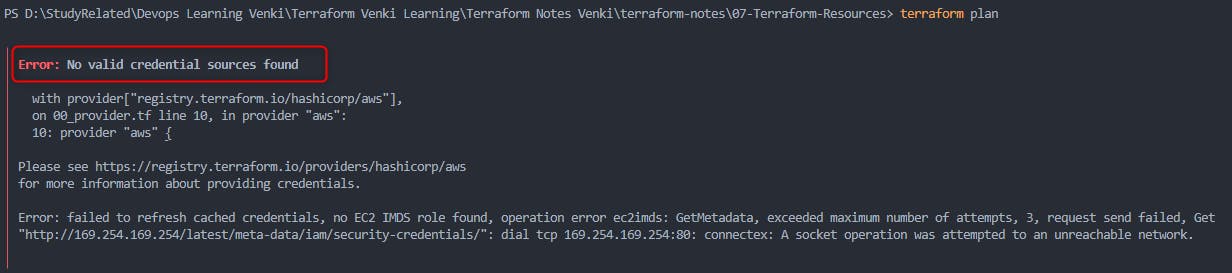
setup AWS Credentials using your preferred methods
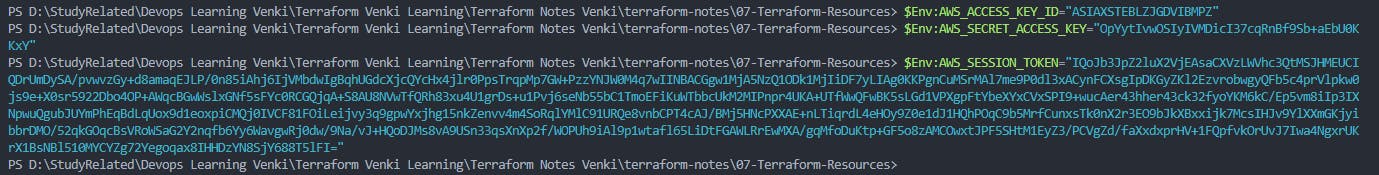
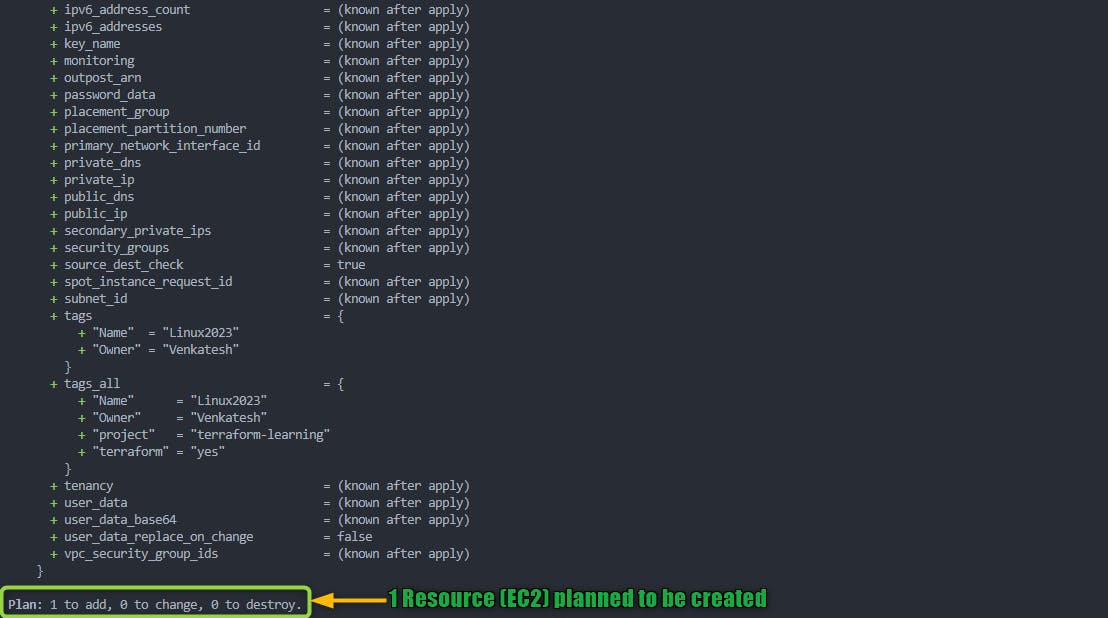
Example of
terraform plan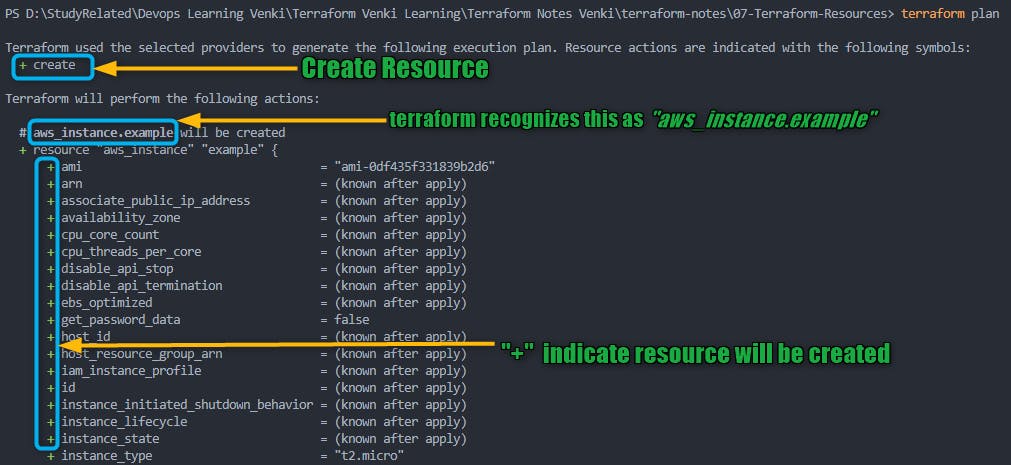
terraform apply: Create Resources by terraformterraform applyis like pressing the "execute" button for your Terraform configuration.It tells Terraform to create, update, or delete resources in your infrastructure based on your configuration.
Be very cautious before you provide approval for
terraform applycommand as it modifies your infrastructureLet's understand
terraform applyin more detail:Execution: Terraform analyzes your configuration and the current state of your infrastructure to identify the differences between the desired state and the actual state.
Changes: Terraform takes action to make the actual state match the desired state, which can involve creating, updating, or deleting resources.
User Confirmation: Before making any changes, Terraform shows you a summary of what it's about to do. It can be over-ridden with auto-approve
User Approval: You must confirm by typing "yes" when prompted to ensure you're aware of the changes.
Execution: Once you confirm, Terraform executes the changes, and you can see the progress in real-time.
Completion: After applying the changes, Terraform provides a summary of what was created, updated, or deleted. It also updates the state file with the current state of your infrastructure.
Example of
terraform apply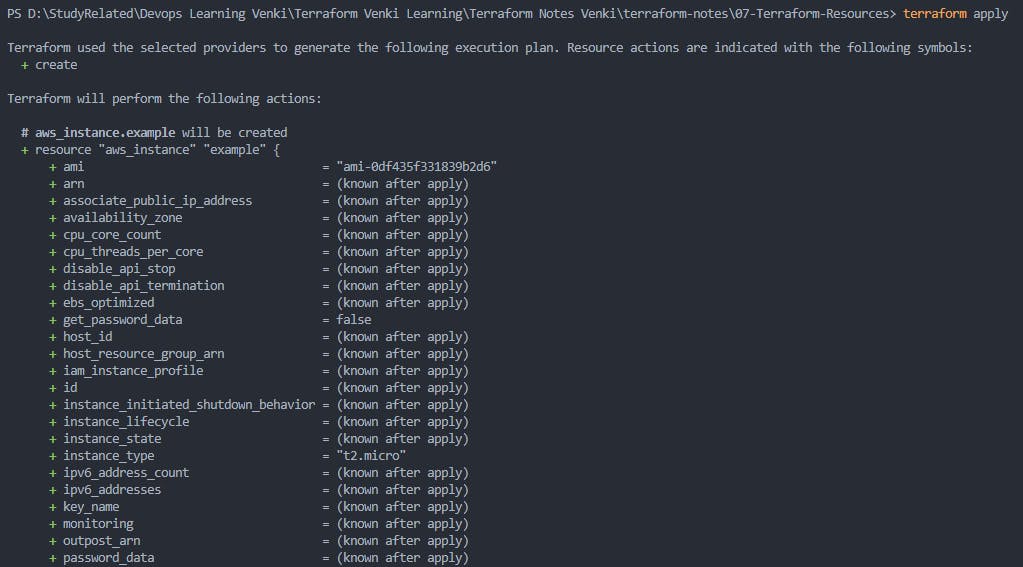
After you type yes to
terraform applyprompt, terraform will start creating resources mentioned in the plan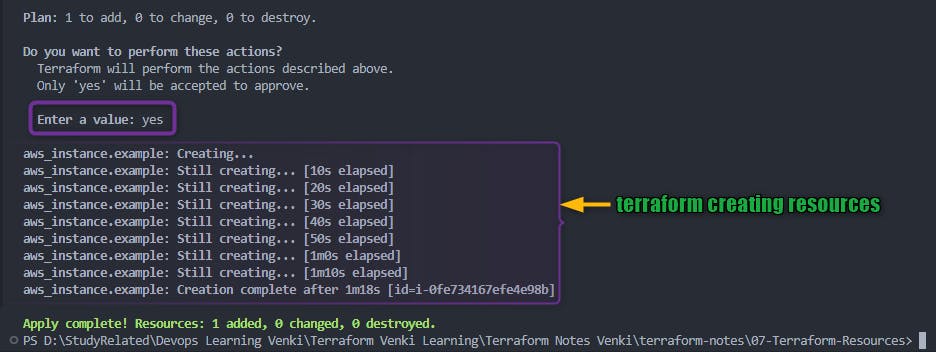
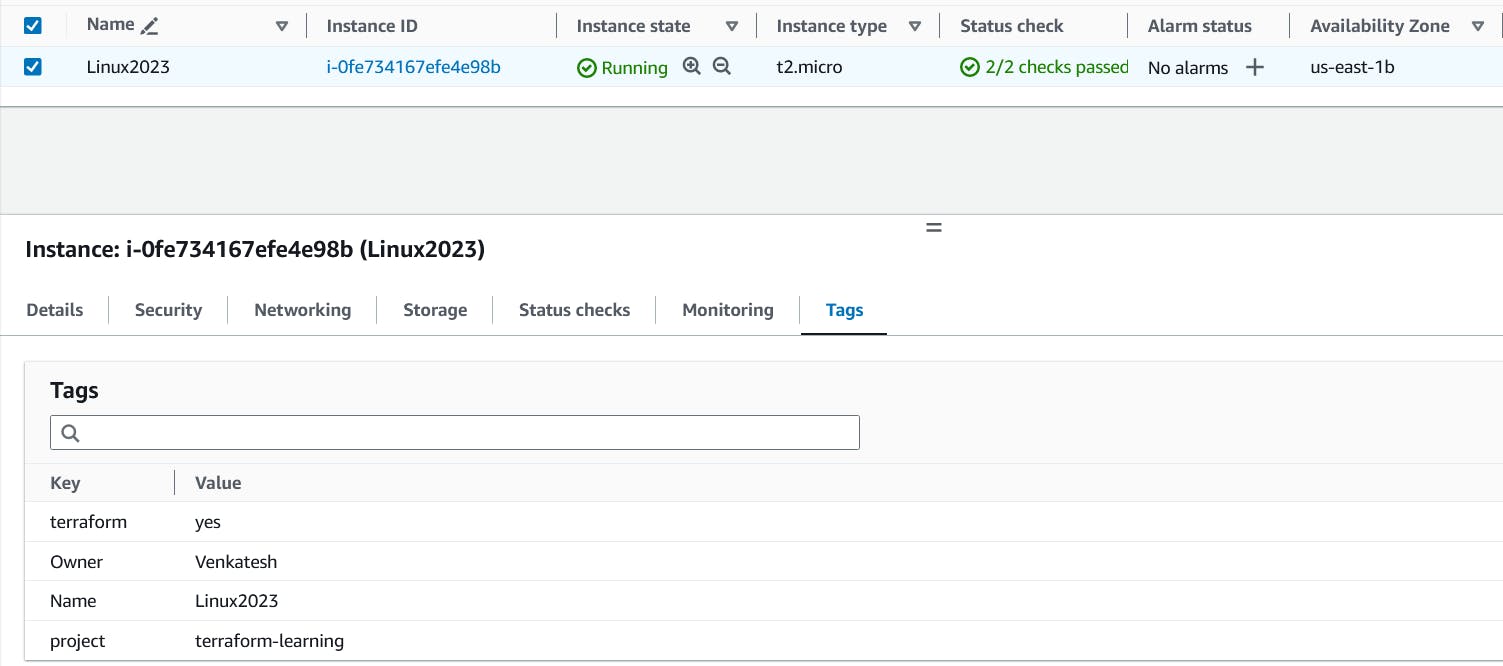
You should also be able to check on your AWS Console resource (EC2) being created

Once terraform completes the execution you should be able to check on your AWS Console resource (EC2) successfully created.
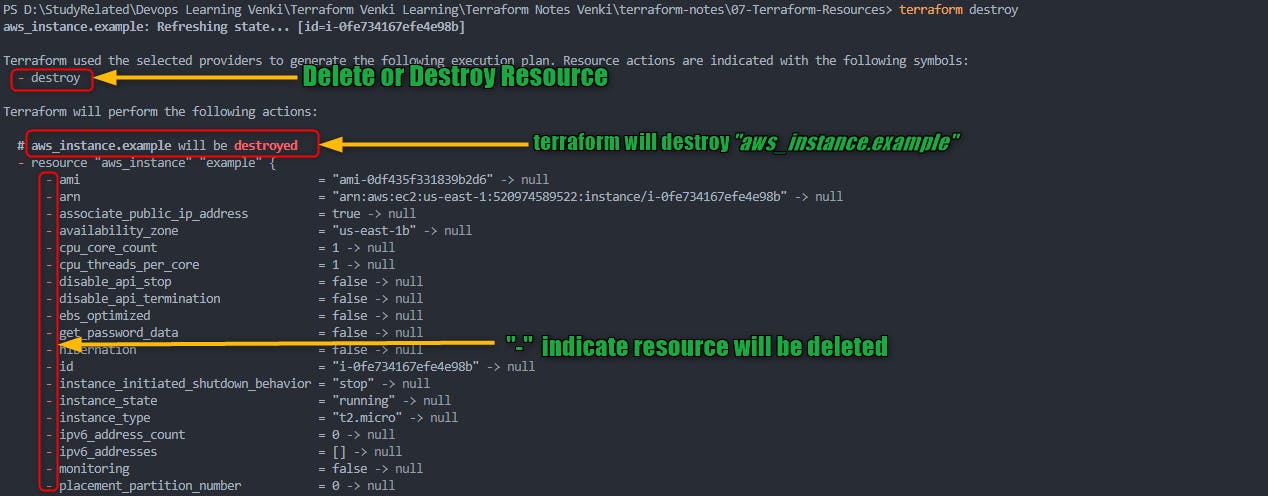
6. terraform destroy: destroy or delete Resources
terraform destroyis like the "off" switch for your Terraform-managed infrastructure.It tells Terraform to tear down and delete all the resources in your infrastructure that were created or managed by Terraform.
Let's understand
terraform destroyin more detail:
1. Execution: Terraform analyzes your configuration and the current state of your infrastructure, just like terraform apply.
2. Resource Destruction: However, instead of creating or updating resources, terraform destroy focuses on destroying and deleting them.
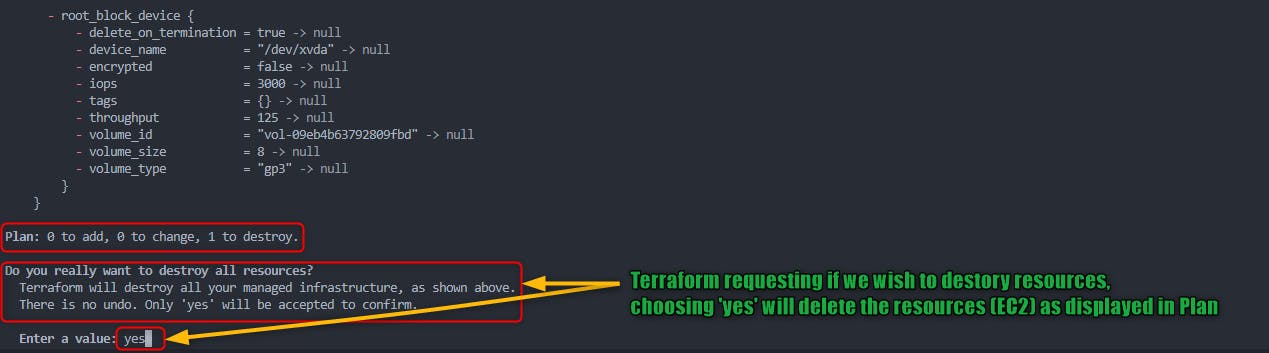
3. User Confirmation: Similar to terraform apply, it shows you a summary of what it's about to destroy. It can be overridden with auto-approve.
4. User Approval: You must confirm by typing "yes" when prompted, ensuring you're aware of the resources that are going to be deleted.
5. Execution: Once you confirm, Terraform executes the destruction, and you can see the progress in real-time.
6. Completion: After the resources are destroyed, Terraform provides a summary of what was deleted.
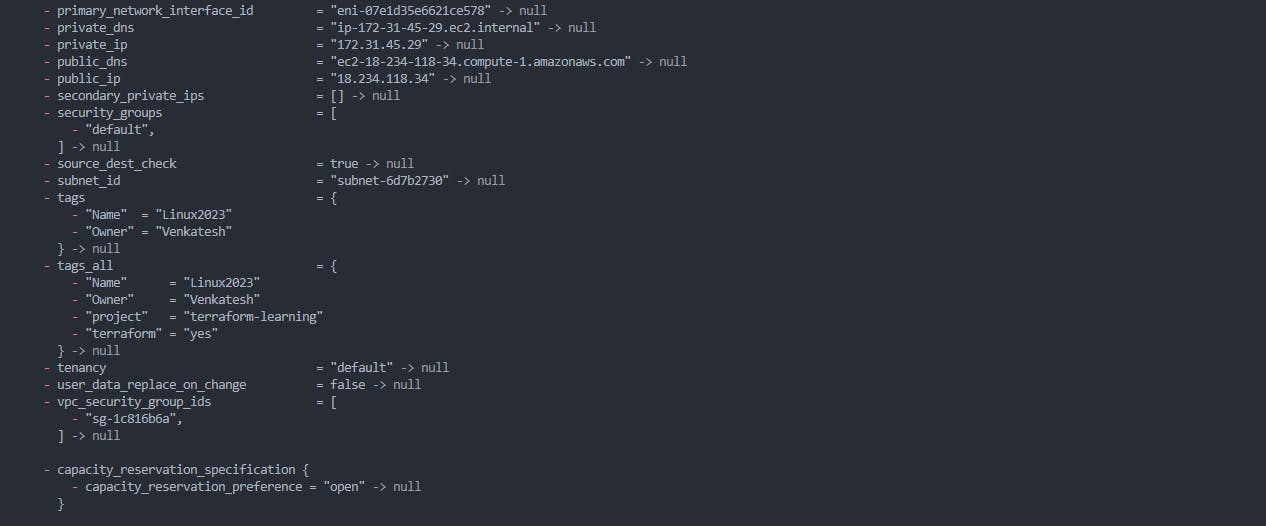
- Example of
terraform destroy
- After you type yes to
terraform destroyprompt, terraform will start destroying resources mentioned in the plan
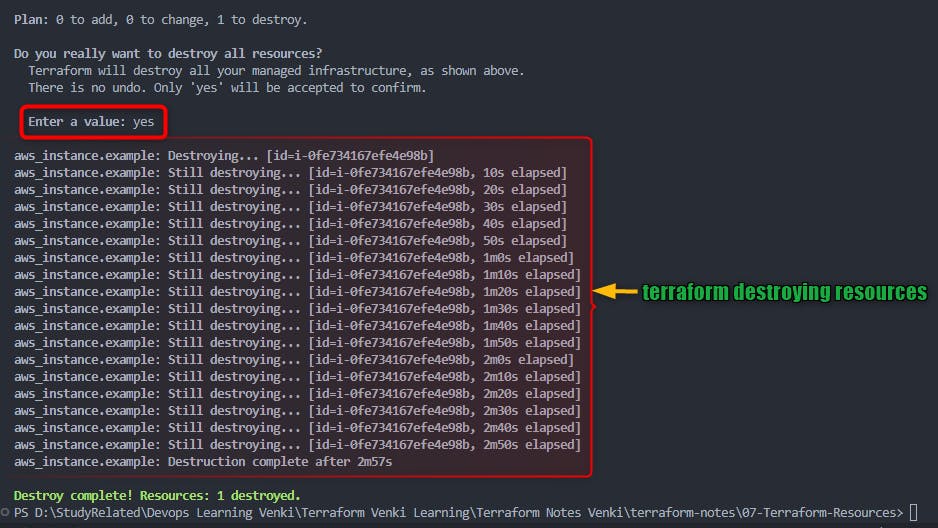
- You should also be able to check on your AWS Console resource (EC2) being shutting down and getting ready for termination

- Once terraform completes the execution you should be able to check on your AWS Console resource (EC2) is successfully terminated.

terraform apply -auto-approve and terraform destroy -auto-approve
The -auto-approve flag is an option that can be added to the terraform apply command to skip the confirmation step.
When you use
terraform apply -auto-approveorterraform destroy -auto-approve, Terraform will not ask for your confirmation and will immediately apply the changes described in the execution plan.This can be useful for automation, scripting, or CI/CD pipelines where manual confirmation is not possible
However, be cautious when using -auto-approve in production environments, as it can lead to unintended changes if the execution plan is not thoroughly reviewed.
Always review the execution plan carefully before using -auto-approve to ensure that the changes are as expected and won't cause any issues in your infrastructure.

