Data Sources
Data resources in Terraform allow you to fetch information or query existing resources outside of the configuration
Data resources do not create or manage infrastructure. They provide a way to reference external data
Immutable Data: Data resources provide a way to interact with external data, but they don't modify that data. They are read-only.
Data Blocks: The structure of a data block is similar to a resource block, but with the
datakeyword.Dynamic Values: You can use dynamic values from data resources in various places within your Terraform configuration.
Syntax:
data "type" "name" {
argument1 = "value1"
argument2 = "value2"
......... = "......"
filter {
name = "<name>"
values = "<value>"
}
filter {
name = "<name>"
values = "<value>"
}
}
Example:
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 5.0"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = var.aws_region
default_tags {
tags = {
Terraform = "yes"
Owner = var.owner
}
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "myec2" {
ami = data.aws_ami.amzn_linux_2023_latest.id # fetching Latest Amazon Linux AMI id from data sources
instance_type = var.ec2_instance_type
tags = {
Name = "Linux2023"
}
}
variable "aws_region" {
description = "AWS Region In Which Resources will be Created"
type = string
default = "us-east-1"
}
variable "owner" {
description = "Name of the Engineer who is creating Resources"
type = string
default = "Venkatesh"
}
# AMI section we are going to use data resources to fetch latest Amazon Linux AMI
/*variable "ec2_ami" {
description = "AWS EC2 AMI Amazon Linux 2023"
type = string
default = "ami-0df435f331839b2d6" # Amazon Linux 2023
}*/
variable "ec2_instance_type" {
description = "EC2 Instance Type"
type = string
default = "t2.micro"
}
data "aws_ami" "amzn_linux_2023_latest" {
most_recent = true
owners = [ "amazon" ]
filter {
name = "name"
values = [ "al2023-ami-2023*" ]
}
filter {
name = "architecture"
values = [ "x86_64" ]
}
filter {
name = "root-device-type"
values = [ "ebs" ]
}
filter {
name = "virtualization-type"
values = [ "hvm" ]
}
}
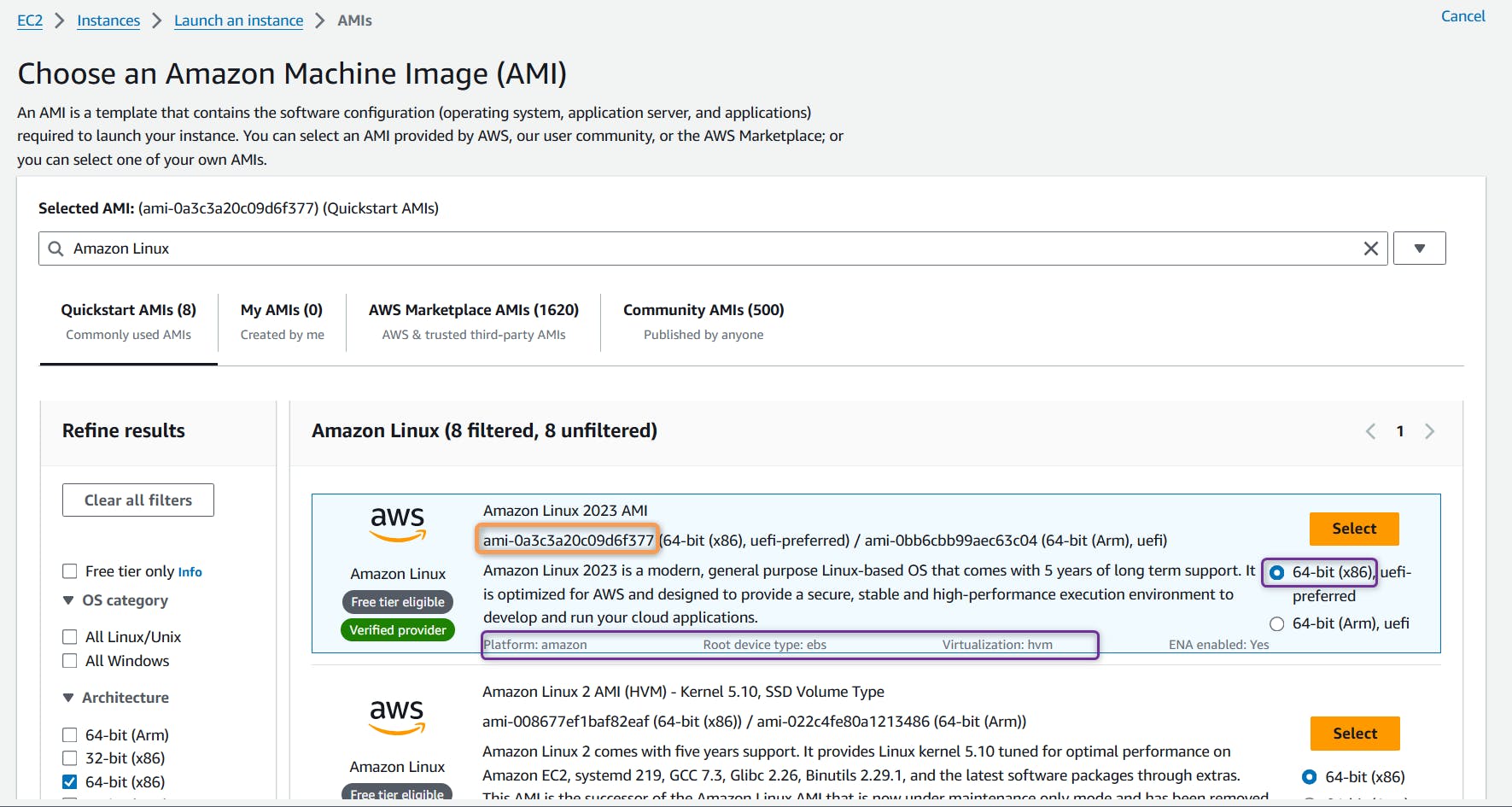
In the above example, We are trying to fetch Latest AWS EC2 Amazon Linux 2023 AMI (located in us-east-1) based on following filters
1.
most_recent=true, to fetch latest AMI
2.name=al2023-ami-2023*to fetch AMI name starting with al2023-ami-2023
3.architecture=x86_64to fetch AMI of type x86_64
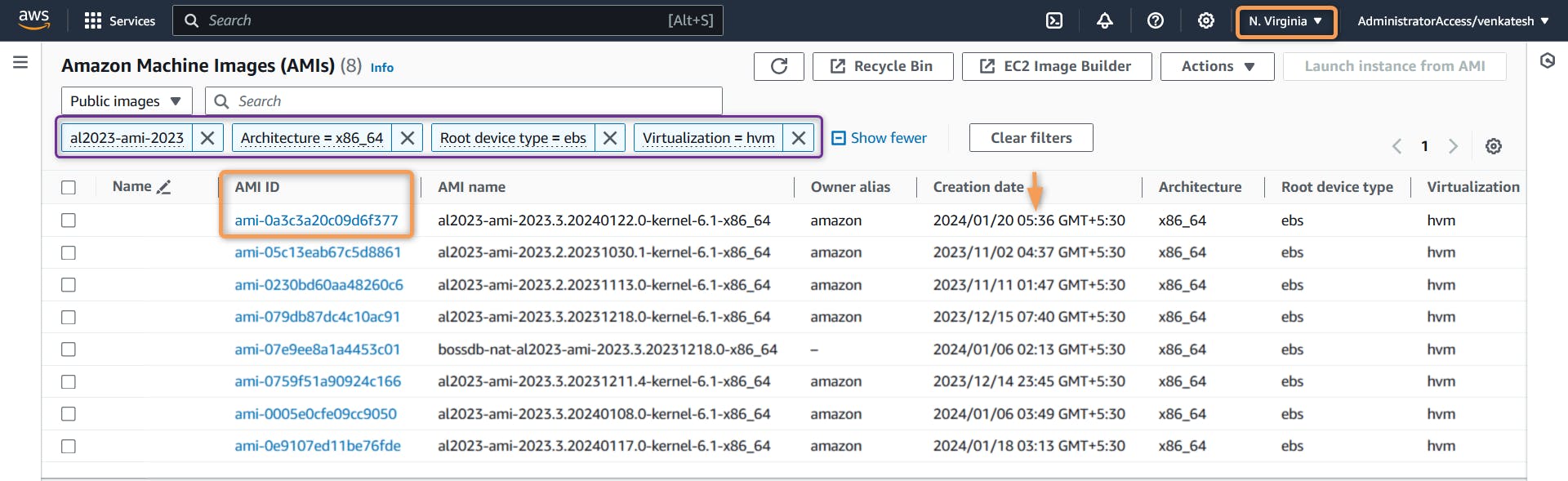
4.root-device-type=ebsto fetch AMI of root device type ebs 5.virtualization-type=hvmto fetch AMI of virtualization type hvmFiltering with similar pattern on AWS Console you should see,
AWS launch Console:
AWS Public AMI Console (EC2 Page ==> AMI):
For additional filter type, Please ref to AWS AWS CLI describe-images
Lets Execute Terraform commands to understand data source behavior
terraform init: Initialize terraformterraform validate: Validate terraform codeterraform fmt: format terraform codeterraform plan: Review the terraform planterraform apply: Create Resources by terraformExample of
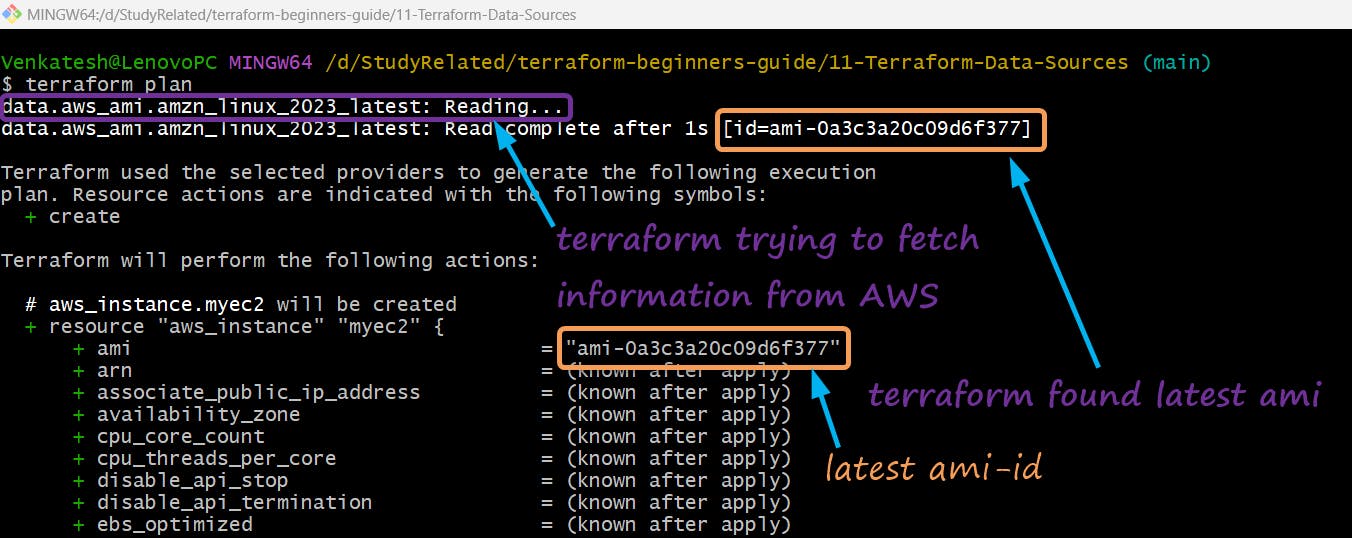
terraform planorterraform applyPlan output shows the Latest AWS EC2 Amazon Linux 2023 AM
terraform apply
$ terraform apply data.aws_ami.amzn_linux_2023_latest: Reading... data.aws_ami.amzn_linux_2023_latest: Read complete after 1s [id=ami-0a3c3a20c09d6f377] Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols: + create Terraform will perform the following actions: # aws_instance.myec2 will be created + resource "aws_instance" "myec2" { + ami = "ami-0a3c3a20c09d6f377" + arn = (known after apply) + associate_public_ip_address = (known after apply) + availability_zone = (known after apply) + cpu_core_count = (known after apply) + cpu_threads_per_core = (known after apply) + disable_api_stop = (known after apply) + disable_api_termination = (known after apply) + ebs_optimized = (known after apply) + get_password_data = false + host_id = (known after apply) + host_resource_group_arn = (known after apply) + iam_instance_profile = (known after apply) + id = (known after apply) + instance_initiated_shutdown_behavior = (known after apply) + instance_lifecycle = (known after apply) + instance_state = (known after apply) + instance_type = "t2.micro" + ipv6_address_count = (known after apply) + ipv6_addresses = (known after apply) + key_name = (known after apply) + monitoring = (known after apply) + outpost_arn = (known after apply) + password_data = (known after apply) + placement_group = (known after apply) + placement_partition_number = (known after apply) + primary_network_interface_id = (known after apply) + private_dns = (known after apply) + private_ip = (known after apply) + public_dns = (known after apply) + public_ip = (known after apply) + secondary_private_ips = (known after apply) + security_groups = (known after apply) + source_dest_check = true + spot_instance_request_id = (known after apply) + subnet_id = (known after apply) + tags = { + "Name" = "Linux2023" } + tags_all = { + "Name" = "Linux2023" + "Owner" = "Venkatesh" + "Terraform" = "yes" } + tenancy = (known after apply) + user_data = (known after apply) + user_data_base64 = (known after apply) + user_data_replace_on_change = false + vpc_security_group_ids = (known after apply) } Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy. Do you want to perform these actions? Terraform will perform the actions described above. Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve. Enter a value: yes aws_instance.myec2: Creating... aws_instance.myec2: Still creating... [10s elapsed] aws_instance.myec2: Still creating... [20s elapsed] aws_instance.myec2: Creation complete after 25s [id=i-0acb2a1d622c55a02] Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed. Venkatesh@LenovoPC MINGW64 /d/StudyRelated/terraform-beginners-guide/11-Terraform-Data-Sources (main)
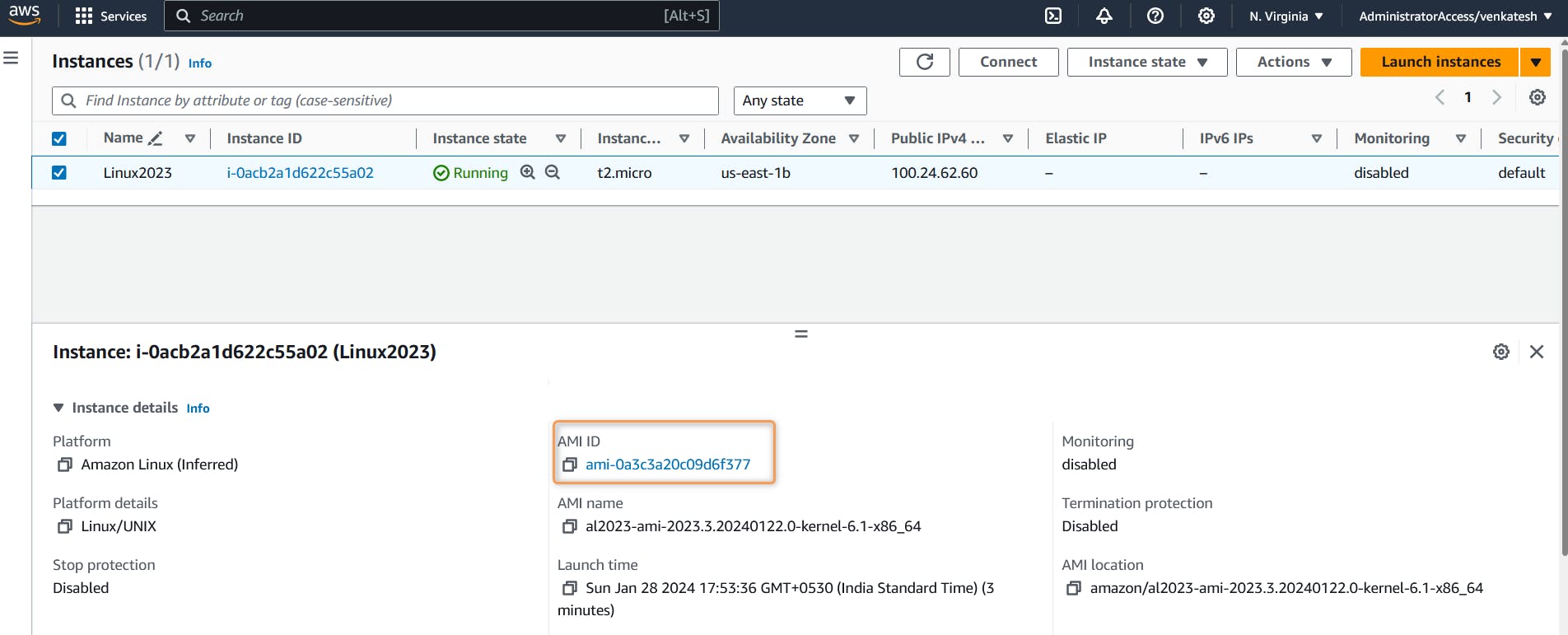
You can now find AWS Console the EC2 instance created using Latest AWS EC2 Amazon Linux 2023 AMI
Let's connect and explore Terraform and AWS.